Funny Kid Running Kicking Self With Own Legs
A gait abnormality is an unusual walking design. Many young children may have an abnormal gait for a period of time as they grow and learn to walk.
Many parents worry well-nigh their children's unusual walking patterns, even so, gait abnormalities are a regular part of physical development. The vast majority of kids abound out of gait abnormalities without medical handling.
When do babies start walking?
Babies typically outset walking when they are effectually 1 year erstwhile. From in that location, they spend the adjacent several years developing remainder and leg strength.
The following historic period ranges are considered average for developmental milestones. Some children accomplish these milestones earlier and some achieve them later. If you are concerned virtually your baby's physical development, talk with your pediatrician.
Developmental milestones
- Around 6 months, about babies can sit with back up and curlicue over
- Around 9 months, most babies learn to crawl.
- Around 9-12 months, most babies volition pull themselves up to continuing past holding onto furniture. Babies at this stage tin can walk with support just can't nevertheless walk on their own.
- By 11-xvi months, most babies volition start to walk without support.
- By 2 years, most toddlers tin go up stairs 1 at a time and jump in place.
- By three years, nearly children can go up stairs reciprocally and stand up on one human foot.
- By four years, most children can go down stairs reciprocally and hop on ane foot.
What are the almost mutual types of pediatric gait abnormalities?
The most common types of gait abnormalities in children are intoeing and outtoeing.
- Intoeing is walking with the feet turned inward.
- Outtoeing is walking with the anxiety turned outward.
Intoeing and outtoeing are commonly not painful.
Several common weather condition tin cause your child's feet to turn inwards or outward in their early years, including tibial torsion and femoral rotation (described below). Each of these conditions typically improve on their own during childhood.
What causes pediatric gait abnormalities?
Tibial torsion
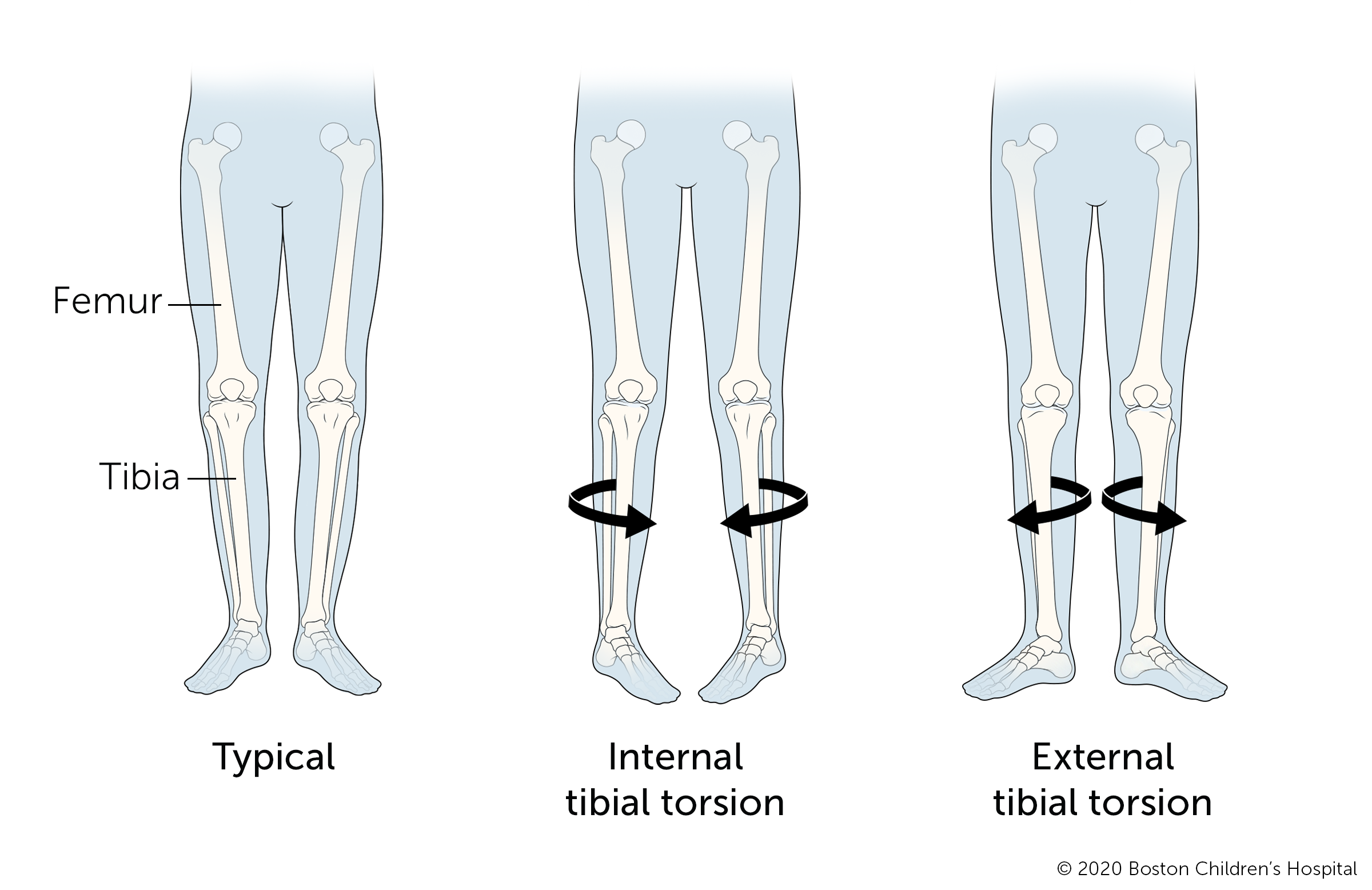
Tibial torsion is the turning of a child'south lower leg (tibia) either inward (internal tibial torsion) or outward (external tibial torsion). The condition often improves without treatment, usually before a child turns iv.
Some children with tibial torsion clothing a night brace betwixt xviii to 30 months old, but this is not common. Doctors only consider surgery for tibial torsion if a child still has the status when they are 8 to 10 years quondam and having meaning walking problems.
Femoral version
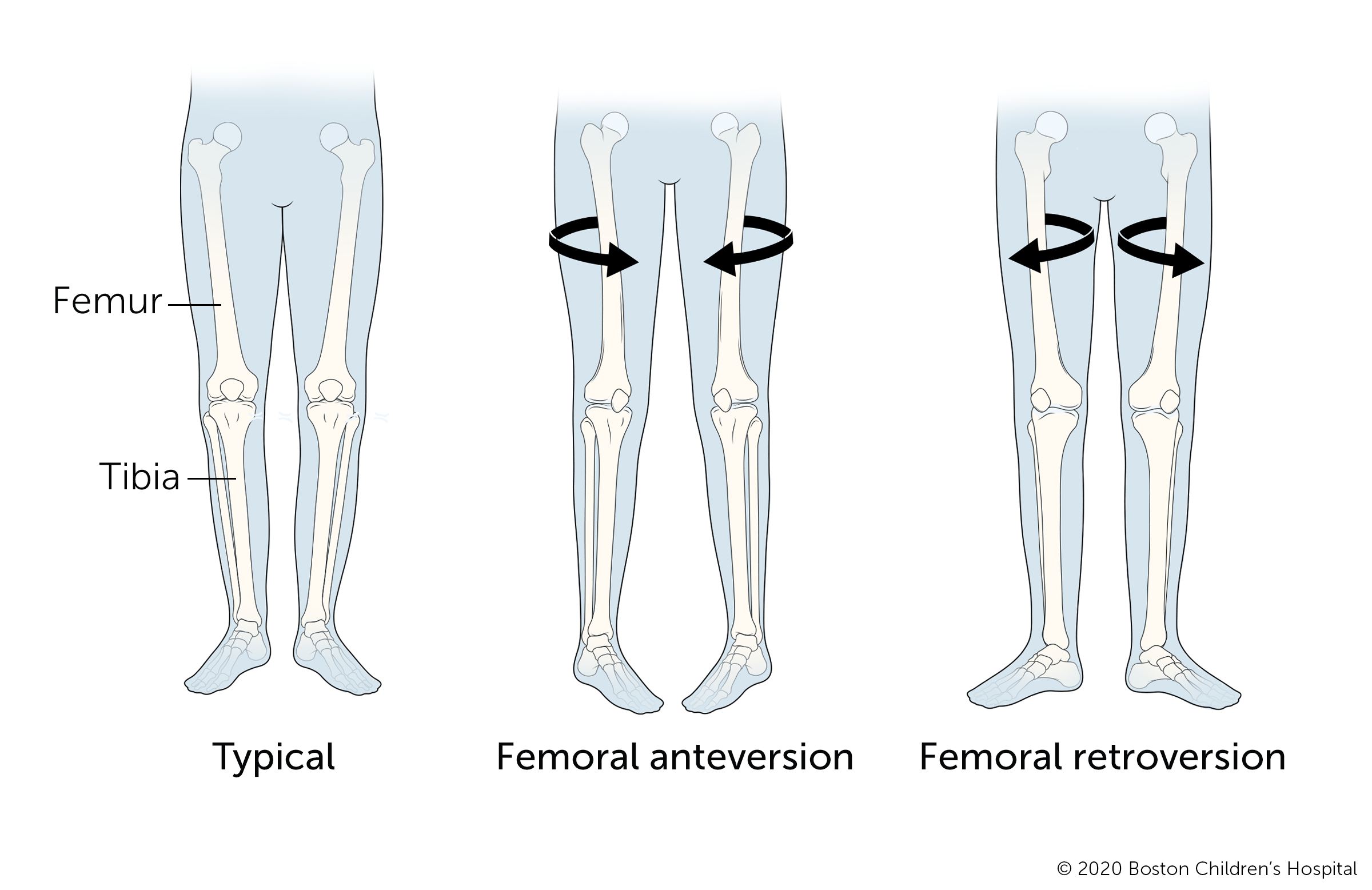
Femoral version describes a kid's upper leg bone (femur) that twists inward or outward. Inwards twisting of the femur (femoral anteversion) causes the feet to bespeak in. Signs of femoral anteversion usually first become noticeable when a child is between 2 to 4 years old, a time when inward rotation from the hip tends to increase. The status usually gets better without handling.
Outward twisting of the femur is called femoral retroversion and causes the feet to betoken outward. It is less mutual than femoral anteversion. In some cases, femoral retroversion may filibuster a child'southward walking, however, the condition often gets better without medical intervention.
Doctors consider surgery for femoral anteversion or femoral retroversion only if a child is older than 9 and has a very astringent status that causes a lot of tripping and an unsightly gait.
Bowlegs and knock knees
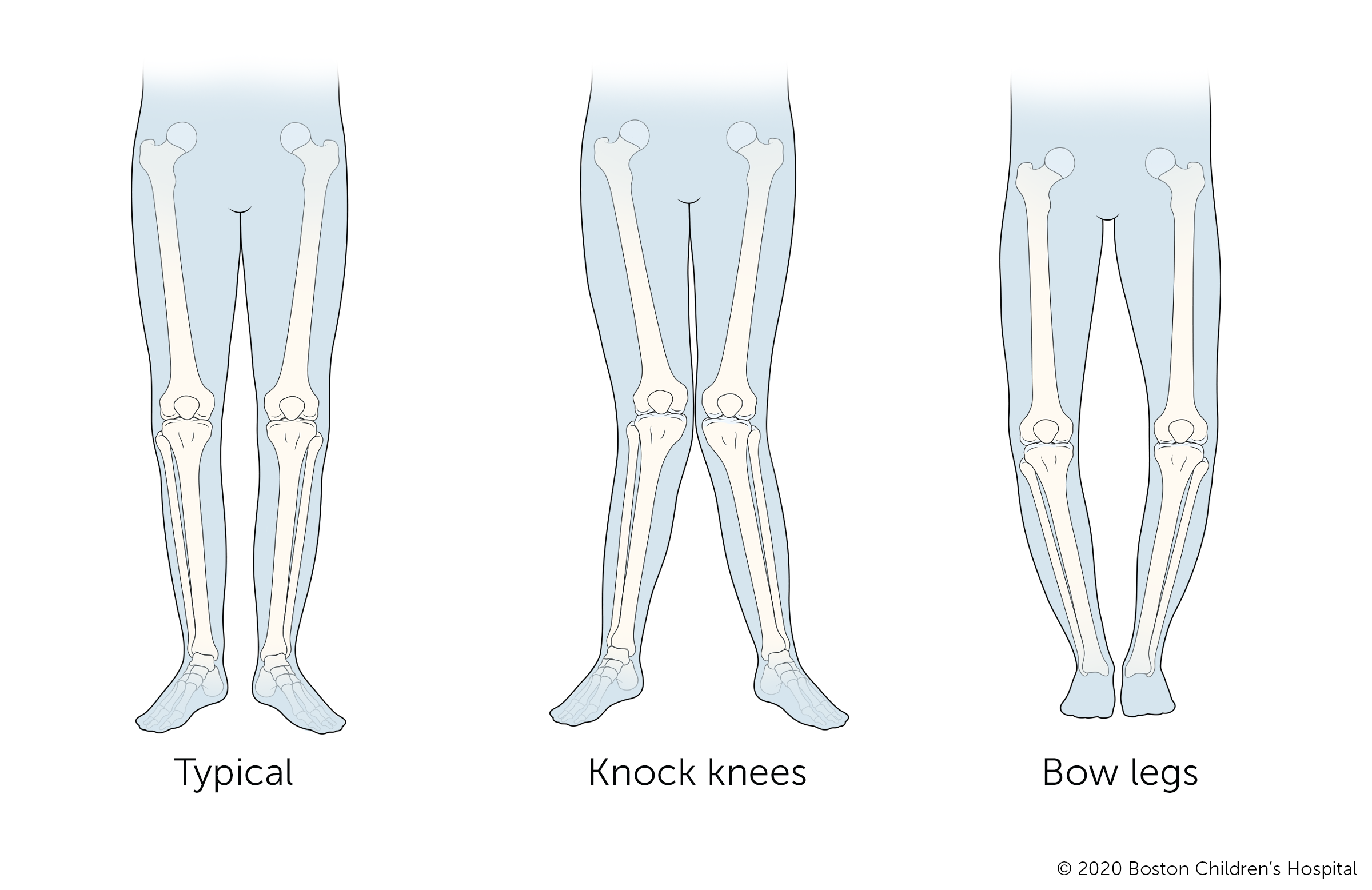
Bowlegs is an outward curve of the legs at the knees. Knock knees is an in curve of the legs at the knees. Both bowlegs and knock knees are common stages of development and commonly self-correct as a child grows.
Flatfeet
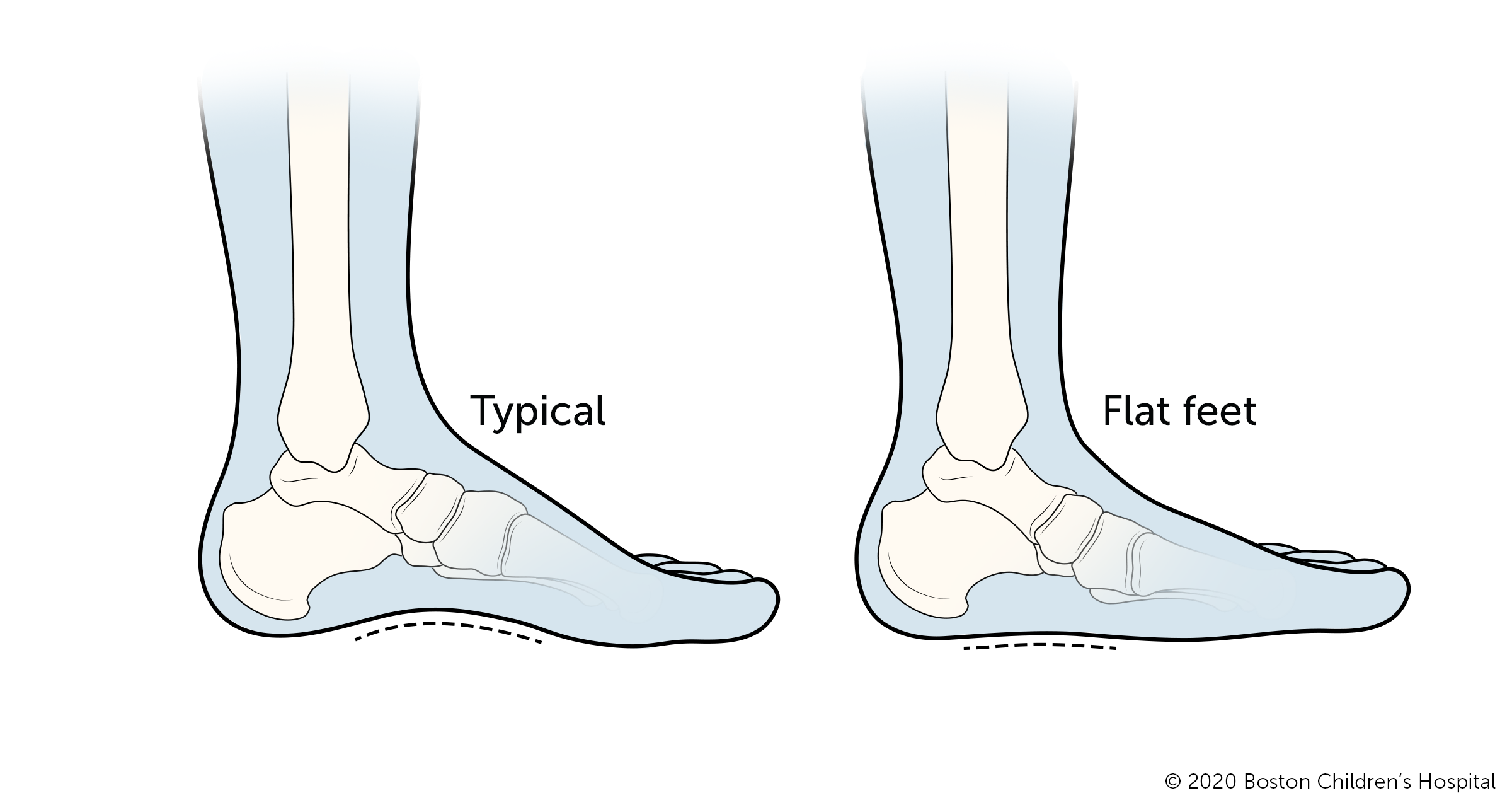
Flatfeet are normal in infants and immature children. Children accept flat feet when the arches in their anxiety have not even so developed and their entire feet press against the floor. The arches develop throughout childhood until well-nigh age x.
Metatarsus adductus
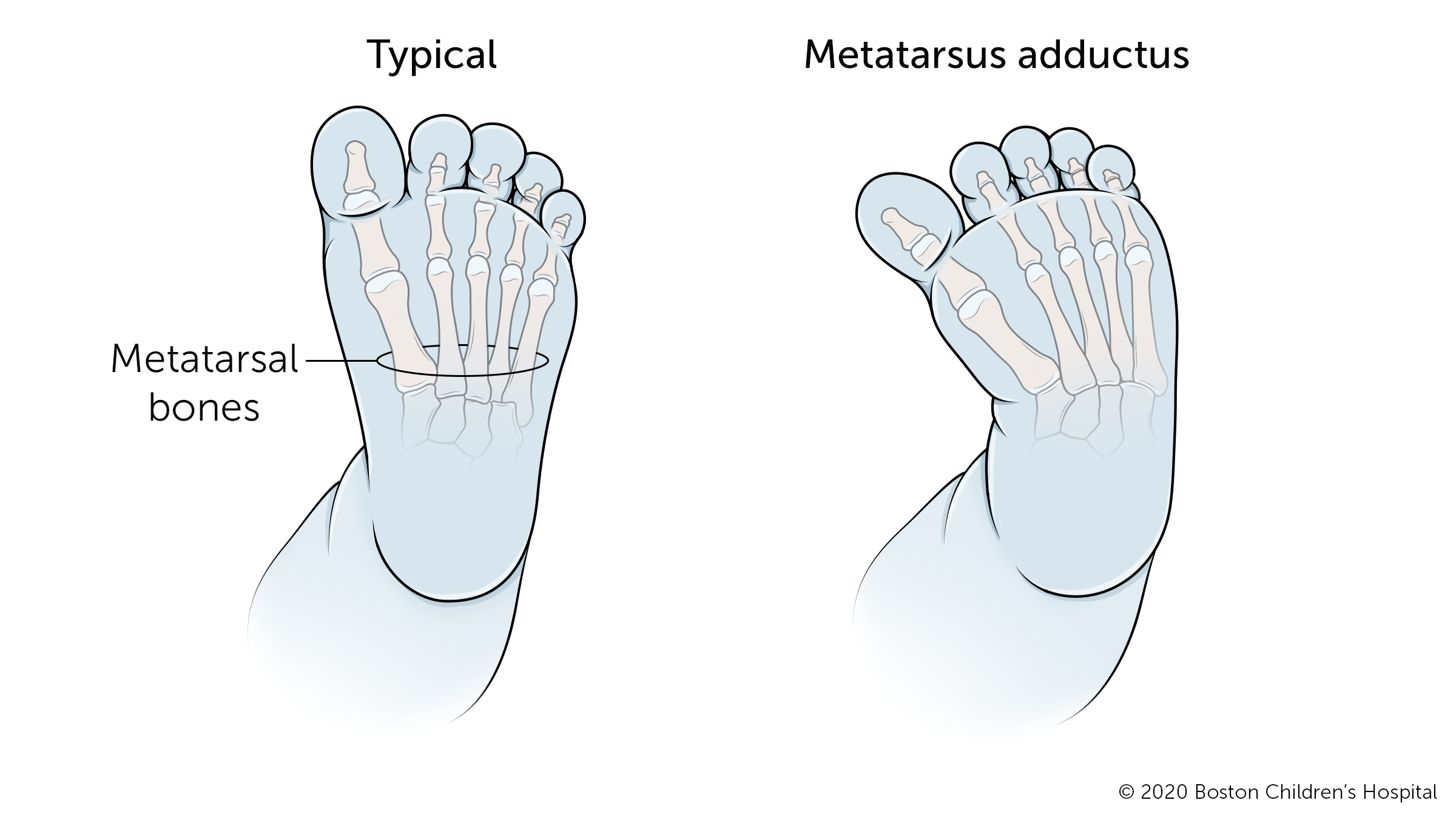
Metatarsus adductus is a common positional deformity that causes a kid's feet to bend inward from the centre of the foot to the toes. In severe cases, it may resemble clubfoot. The condition improves on its own most of the time.
Babies with severe metatarsus adductus may need handling, which usually involves special exercises, casts, or special cosmetic shoes. These treatments take a high charge per unit of success in babies from half-dozen to ix months old.
Limping
Sudden limping is most probable due to hurting caused by a small-scale, easily treated injury. Splinters, blisters, or tired muscles are common culprits. Less frequently, limping can involve a more serious trouble such as a sprain, fracture, dislocation, joint infection, or autoimmune arthritis. In rare cases, a limp may be the start sign of a tumor.
Non-painful chronic limping may be sign of developmental problem, such equally a leg length discrepancy or hip dysplasia or a neuromuscular trouble, such as cognitive palsy.
Toe walking
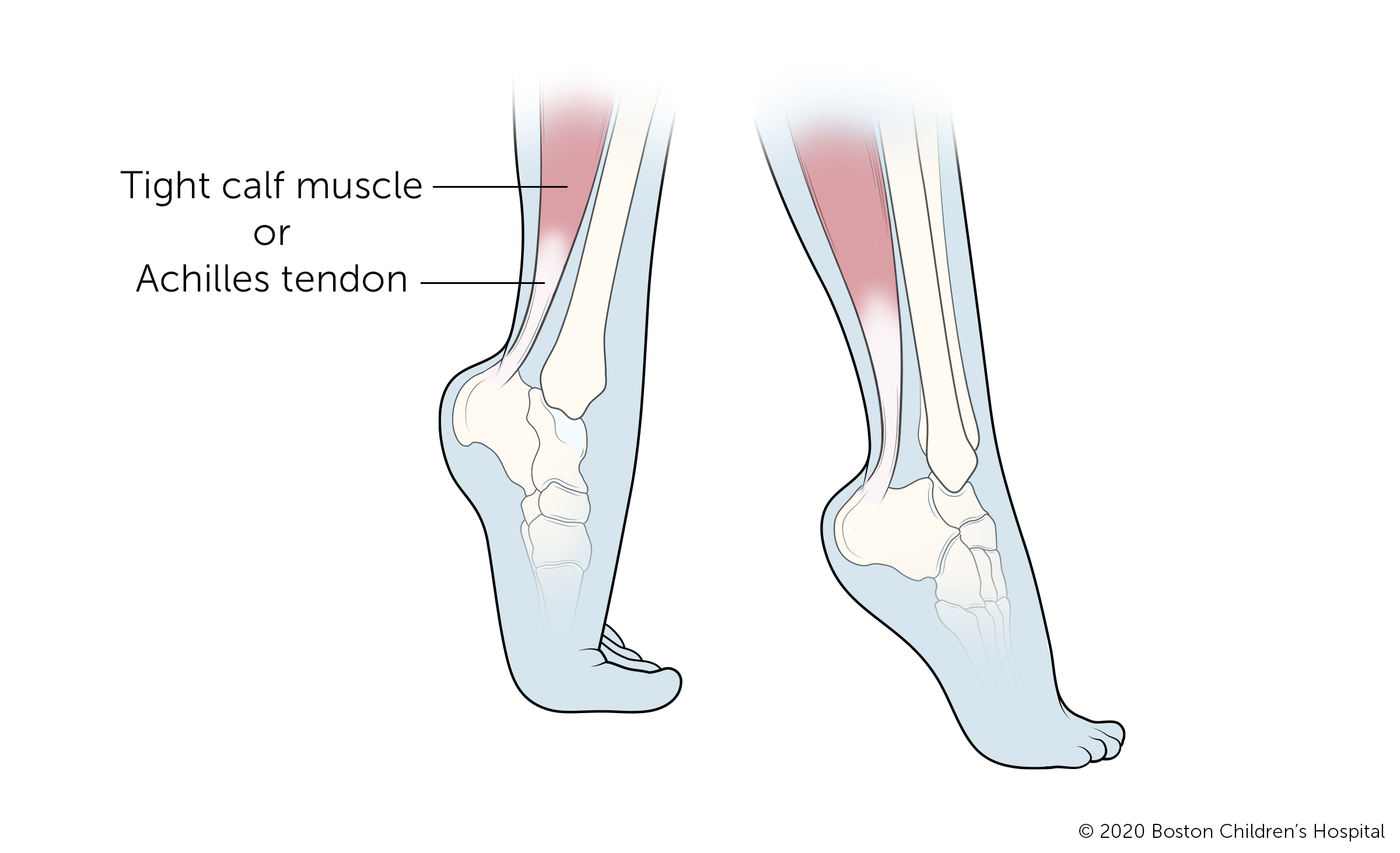
Toe walking is a common gait aberration, particularly in young children who are just starting to walk. In most cases, this will resolve on its ain over fourth dimension without intervention. Even so, children who walk normally for a period then later begin to walk on their toes, or children with tightness of their Achilles tendons, should be evaluated by a physician.
Many cases of persistent toe-walking run in families or are caused by tight muscles. Handling may involve observation, physical therapy, bracing, casting, or surgery. In some cases, toe-walking may indicate a neuromuscular disorder such as cerebral palsy or it could be a sign of developmental dysplasia of the hip or leg length discrepancy.
How are gait abnormalities diagnosed?
Your child's doc volition perform a physical test and watch your child every bit they walk or run. They may look to see whether your child's legs are shaped the same or differently. They may likewise ask if your child shows any signs of being in pain when they walk and whether whatever members of your shut family unit have had long-term walking problems.
Other diagnostic procedures may include:
- X-ray: A diagnostic exam that produces images of internal tissues, basic, and organs that can exist used to look at bone structure and alignment.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A diagnostic process that produces detailed images of soft tissues and structures within the trunk. This test is sometimes used to rule out whatever associated abnormalities of the spinal cord and nerves.
- Computerized Tomography browse (also called a CT or CAT scan): A diagnostic imaging process that shows detailed images of the bones and joints.
How are pediatric gait abnormalities treated?
In near cases, a child with an abnormal gait is observed over the course of several years. The doctor volition monitor your child's walking patterns to ensure their legs continue to develop and their walking patterns go more than typical over fourth dimension. Fortunately, most causes of gait abnormalities volition resolve without any intervention as a kid grows.
If a gait abnormality is caused by an injury or developmental status, your child's dr. will treat that condition. Treatment for gait abnormalities that practise not resolve may include surgery and is something to discuss with your medico.
How nosotros care for gait abnormalities at Boston Children's Hospital
The Lower Extremity Plan at Boston Children's Hospital offers comprehensive assessment, diagnosis, and handling for children of all ages with weather affecting their lower limbs. We have extensive experience treating disorders of the feet, ankles, knees, legs, and hips. Whether the patient is an baby, kid, or boyish, our goal is to help children alive full, contained lives.
Source: https://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions/walking-gait-abnormalities
0 Response to "Funny Kid Running Kicking Self With Own Legs"
Post a Comment